It’s the season of climate talks and renewed pushes for businesses to adopt more aggressive strategies to cut greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across their value chain. As Climate Week and the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) close out high-level talks in New York City, preparations begin for the UN Climate Change Conference (COP) in November, where world leaders will assess the progress of Net Zero targets and discuss solutions for the urgent issue of climate change.
With these high-level meetings will trickle down the renewed calls for organisations to ensure they are implementing climate strategies and working to reduce their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in line with Paris Agreement targets, which aim to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Businesses and their supply chains are increasingly under this demand for reduced emissions from their operations, as data shows supply chains generate around 60% of the world’s GHG output. Amid the UNGA, the United Nations released a ‘Pact for the Future’ to reaffirm sustainability pledges and declare actions toward a more sustainable and inclusive world. A key declaration in this report included ‘accelerating action’ toward Paris Agreement targets, rapidly reducing GHG emissions and calling on parties to contribute to global climate efforts.
Getting to grips with Scope 3
For businesses, more and more climate requirements are focusing on not only Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, which refer to emissions related to more direct operations, but also Scope 3, or the indirect emissions relating to supply chain partners across the value chain.
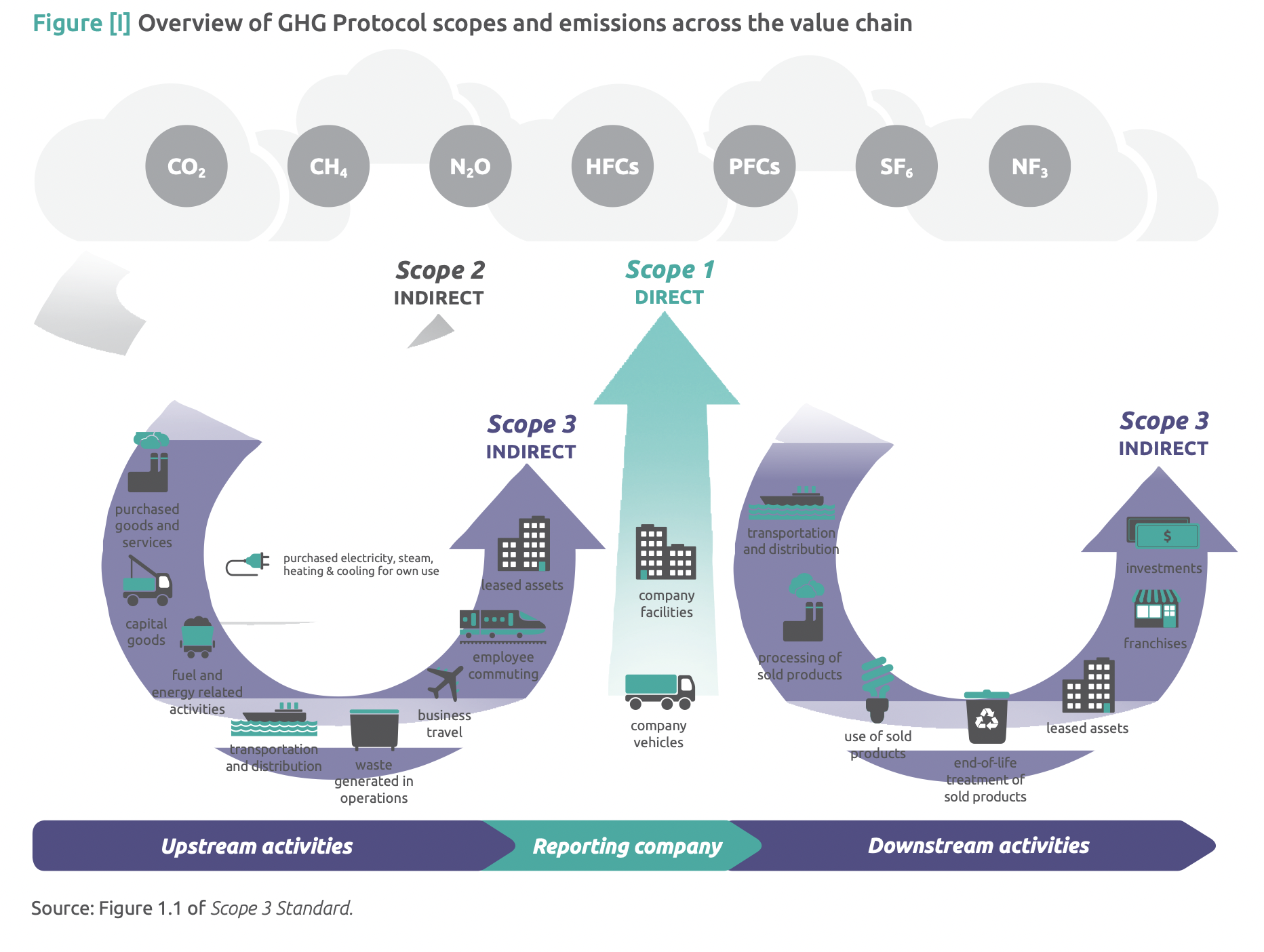 Source: GHG Protocol Scope 3 Calculation Guidance PDF
Source: GHG Protocol Scope 3 Calculation Guidance PDF
We know that supply chain complexity, data quality, and inefficient resources create challenges around tracking Scope 3 emissions. But to refocus on carbon data tracking and management, we recommend prioritising the following to get started:
- Get your data in check: Tracking and managing your supply chain’s GHG emissions will only be as effective as the quality of your data. Organisations must prioritise consolidating their data and implementing quality data management systems to ensure they have an accurate view of where targeted emissions reductions can occur.
- Establish science-based targets: Science-based targets help companies establish targets for climate action based on the latest climate science, aligned to the Paris Agreement goals and are established in the context of a company’s individual sector and market share.
- Engage suppliers: A supply chain is only as effective as its weakest link. Therefore, organisations must engage and align every supply chain partner to ensure actions and emissions reduction strategies are aligning with the company’s targets.
- Increase transparency: Data quality and transparency will continue to be a key driver in implementing real change and enabling climate progress. Measuring a company’s current emissions accurately is the only way to establish effective targets and cut carbon emissions with intent and to understand where in the supply chain emissions reduction must be prioritised.
In a regulatory environment increasingly attuned to the broader ecological footprint of businesses, the need for comprehensive Scope 3 emissions tracking has never been more pressing. By prioritising this component of sustainability in both business strategies and accurate data reporting, organisations position themselves as responsible entities of the environment, fostering resilience, credibility, and long-term viability.
Centralising carbon data through EiQ
Our supply chain due diligence software EiQ introduces an environmental module, which allows businesses to view and monitor their supply chain's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and environmental data.
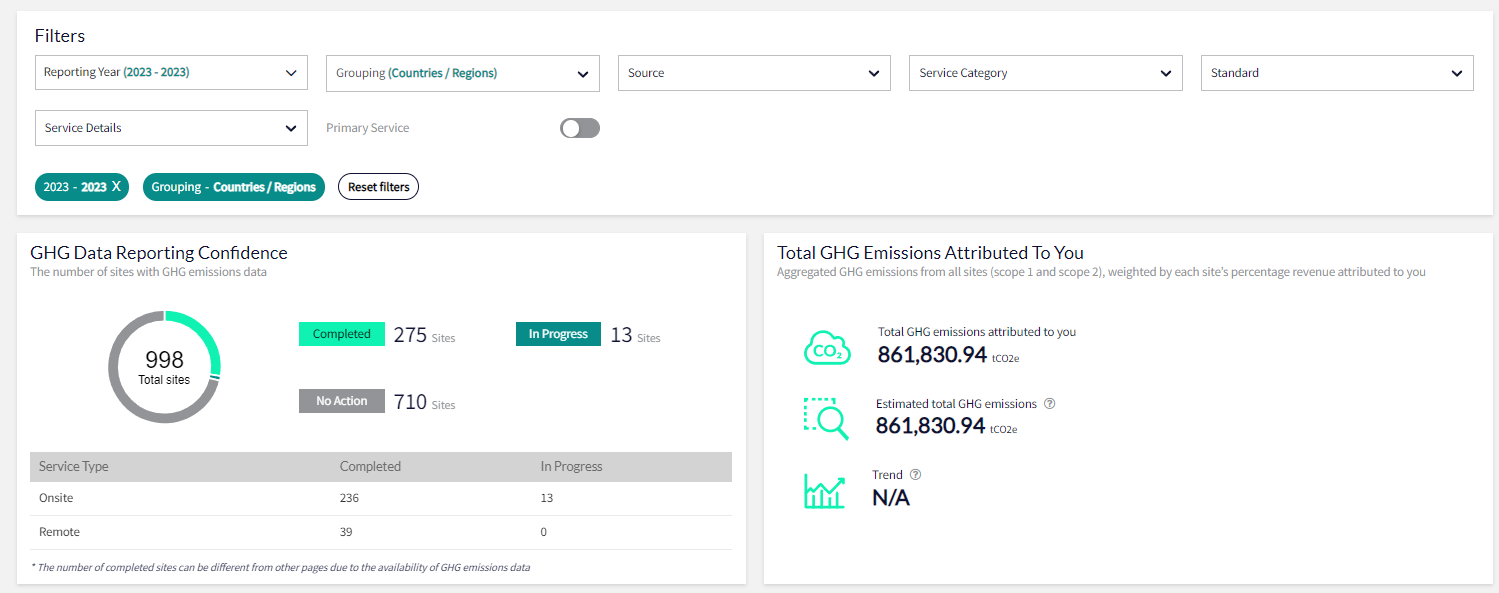 EiQ environmental page sample
EiQ environmental page sample
This function gives companies a high-level overview of their GHG emissions and helps them to understand the full scope of their environmental impact with clear, actionable data. EiQ’s environmental module also shows an organisation’s estimated total of supply chain’s emissions, which calculates the projected GHG emissions utilising the company’s current and estimated data.
Only 22% of CFOs are prepared for climate reporting and assurance requirements, according to a new survey, and with the rise of regulations, monitoring and managing environmental data is crucial. Quantifying and addressing such categories of emissions requires close engagement, cooperation and collaboration across the value chain. Engaging all parties, from internal procurement teams to external suppliers and vendors, is essential to obtain accurate data for initial emissions quantifications.
Our goal is to provide businesses with the tools and insights needed to manage their supply chain’s environmental impact effectively. EiQ’s environmental module is designed to help companies meet sustainability goals, adhere to regulatory requirements, and demonstrate your commitment to responsible sourcing.
Request a free demo to learn how to track and manage your carbon footprint through EiQ.
